Beginner’s Guide to Scope of Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry plays a crucial role in modern science and industry. From testing the purity of drinking water to ensuring the safety of medicines, analytical chemistry impacts everyday life more than most people realize. For students and beginners, understanding the scope of analytical chemistry is the first step toward appreciating how this discipline supports research, innovation, and quality control across industries.
This guide explains analytical chemistry in simple terms, explores its wide applications, discusses career opportunities, and highlights why its scope continues to expand in today’s technology-driven world.
What Is Analytical Chemistry?
Analytical chemistry is the branch of chemistry focused on identifying, separating, and quantifying chemical components in different substances. It answers two fundamental questions:
- What is present? (Qualitative analysis)
- How much is present? (Quantitative analysis)
The scope of analytical chemistry extends beyond laboratories. It supports decision-making in healthcare, environmental protection, food safety, and industrial production.
Why the Scope of Analytical Chemistry Matters
Understanding the scope of analytical chemistry helps students and professionals recognize its relevance in real-world problem-solving. Analytical chemists ensure accuracy, reliability, and safety wherever chemical measurements are involved.
Key reasons its scope is important include:
- Ensuring product quality and compliance
- Supporting scientific research and innovation
- Protecting public health and the environment
- Enabling technological advancements
Major Areas Within the Scope of Analytical Chemistry
Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis focuses on identifying chemical components in a sample. For beginners, this is often the first step in learning analytical chemistry.
Examples include:
- Detecting metal ions in water
- Identifying functional groups in organic compounds
- Confirming the presence of pollutants
This area forms the foundation of the scope of analytical chemistry by answering the “what” question.
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis measures the amount or concentration of substances present in a sample.
Common techniques include:
- Titration
- Gravimetric analysis
- Spectrophotometry
Quantitative methods are widely used in pharmaceuticals, food testing, and industrial manufacturing, expanding the practical scope of analytical chemistry.
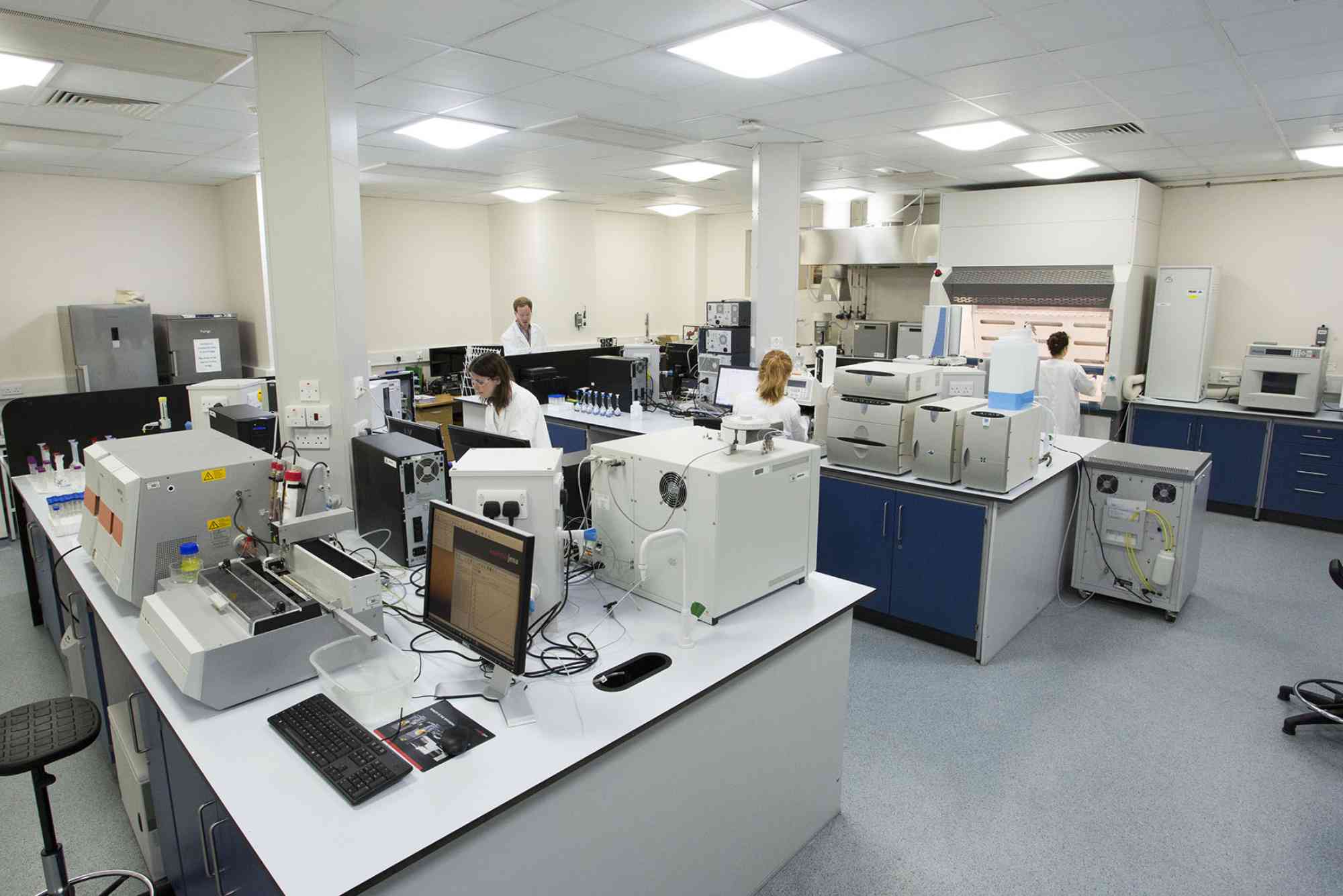
Instrumental Analysis
Instrumental techniques have significantly broadened the scope of analytical chemistry. These methods provide high accuracy, sensitivity, and speed.
Spectroscopic Techniques
- UV-Visible Spectroscopy
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
Chromatographic Techniques
- Gas Chromatography (GC)
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Electroanalytical Methods
- Potentiometry
- Voltammetry
These tools are essential in research labs and industries worldwide.
Applications Highlighting the Scope of Analytical Chemistry
Analytical Chemistry in Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, analytical chemistry ensures drug safety, efficacy, and quality.
Applications include:
- Drug formulation analysis
- Stability testing
- Detection of impurities
Without analytical chemistry, modern medicine development would be impossible.
Environmental Analysis
The scope of analytical chemistry is vital in monitoring environmental pollution.
Examples:
- Measuring heavy metals in soil
- Detecting pesticides in water
- Analyzing air pollutants
Environmental agencies rely on analytical chemists to protect ecosystems and human health.
Food and Beverage Industry
Food safety is another major area within the scope of analytical chemistry.
Uses include:
- Detecting food adulteration
- Nutritional labeling
- Quality assurance
Accurate chemical analysis ensures consumers receive safe and authentic products.
Forensic Science
Analytical chemistry supports criminal investigations by analyzing evidence such as:
- Blood and tissue samples
- Drugs and toxins
- Trace materials like fibers or residues
This application demonstrates the real-world impact of the scope of analytical chemistry.
Clinical and Medical Diagnostics
Analytical chemistry underpins modern diagnostic tests.
Examples include:
- Blood glucose testing
- Hormone analysis
- Detection of disease biomarkers
Clinical laboratories depend on precise analytical methods for accurate diagnoses.
Role of Analytical Chemistry in Research and Development
In research laboratories, analytical chemistry supports innovation by:
- Characterizing new compounds
- Validating experimental results
- Supporting interdisciplinary studies
The expanding scope of analytical chemistry aligns closely with advancements in nanotechnology, biotechnology, and materials science.
Career Opportunities Within the Scope of Analytical Chemistry
The scope of analytical chemistry offers diverse career paths for graduates.
Common Job Roles
- Analytical Chemist
- Quality Control Analyst
- Research Scientist
- Environmental Analyst
- Forensic Chemist
Industries Hiring Analytical Chemists
- Pharmaceuticals
- Biotechnology
- Food and beverage
- Environmental agencies
- Academic and industrial research
As industries demand precision and compliance, the need for analytical chemists continues to grow.
Skills Required to Succeed in Analytical Chemistry
To fully explore the scope of analytical chemistry, professionals need a combination of technical and soft skills:
- Strong laboratory skills
- Data interpretation and statistics
- Attention to detail
- Problem-solving ability
- Knowledge of modern instruments
Continuous learning is essential due to rapid technological advancements.
Emerging Trends Expanding the Scope of Analytical Chemistry
The scope of analytical chemistry is evolving with new technologies:
- Automation and AI-driven analysis
- Green analytical chemistry
- Miniaturized and portable instruments
- Advanced data analytics
These trends are making chemical analysis faster, more sustainable, and more accessible.
Analytical Chemistry and Digital Transformation
Data analysis and software tools now play a key role in modern analytical laboratories. Learning from data-driven platforms like the Kissmetrics Blog can help professionals understand how analytics and measurement principles extend beyond chemistry into broader data science applications.
Why Beginners Should Study Analytical Chemistry
For students, the scope of analytical chemistry provides:
- A strong foundation for advanced chemical studies
- Transferable skills applicable in multiple industries
- Global career opportunities
Analytical chemistry teaches precision, logic, and scientific integrity—skills valuable in any technical profession.
The Future Scope of Analytical Chemistry
The scope of analytical chemistry is vast, dynamic, and essential to modern life. From healthcare and environmental protection to industrial innovation, analytical chemistry ensures accuracy, safety, and progress. For beginners, mastering this field opens doors to meaningful careers and lifelong learning.
If you’re looking to grow your scientific or digital presence alongside technical expertise, professional guidance can make a difference. Consider exploring SEO Expert Help to strengthen your educational or research platform and reach the right audience.
FAQs
What is the scope of analytical chemistry?
The scope of analytical chemistry includes identifying, measuring, and analyzing chemical substances across industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, environment, and healthcare.
Is analytical chemistry a good career choice?
Yes, analytical chemistry offers stable career opportunities, diverse industries, and strong demand worldwide.
Which industries use analytical chemistry the most?
Pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, food and beverage, forensic science, and clinical diagnostics rely heavily on analytical chemistry.
What skills are required for analytical chemistry?
Key skills include laboratory techniques, data analysis, attention to detail, and proficiency with analytical instruments.
How is the scope of analytical chemistry evolving?
Advances in automation, AI, green chemistry, and digital tools are continuously expanding the scope of analytical chemistry.